[HarmonyOS NEXT 实战案例十四] 任务管理看板网格布局(上)
[HarmonyOS NEXT 实战案例十四] 任务管理看板网格布局(上)
项目已开源,开源地址: https://gitcode.com/nutpi/HarmonyosNextCaseStudyTutorial , 欢迎fork & star
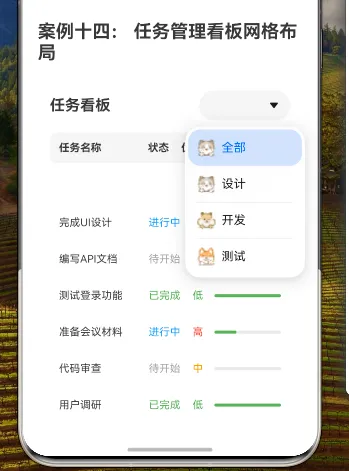
效果演示
1. 概述
本教程将详细讲解如何使用HarmonyOS NEXT的GridRow和GridCol组件实现一个任务管理看板的网格布局。任务管理看板是项目管理中常用的工具,通过网格布局可以清晰地展示任务信息,包括任务名称、状态、优先级和进度等。
本教程将涵盖以下内容:
- 任务数据结构设计
- 整体布局实现
- 标题和筛选功能
- 表头设计
- 任务列表实现
- 状态和优先级的视觉区分
2. 数据结构设计
首先,我们需要定义任务的数据结构,包含任务的基本信息:
interface TaskType {
title: string; // 任务名称
status: string; // 任务状态
priority: string; // 优先级
category: string; // 分类
progress: number; // 进度
}
这个接口定义了任务的五个基本属性:
title:任务名称,如"完成UI设计"、"编写API文档"等status:任务状态,如"已完成"、"进行中"、"待开始"等priority:优先级,如"高"、"中"、"低"等category:分类,如"设计"、"开发"、"测试"等progress:进度,表示任务完成的百分比,范围为0-100
3. 数据准备
接下来,我们准备一些示例任务数据用于展示:
private tasks: TaskType[] = [
{ title: '完成UI设计', status: '进行中', priority: '高', category: '设计', progress: 60 },
{ title: '编写API文档', status: '待开始', priority: '中', category: '开发', progress: 0 },
{ title: '测试登录功能', status: '已完成', priority: '低', category: '测试', progress: 100 },
{ title: '准备会议材料', status: '进行中', priority: '高', category: '管理', progress: 30 },
{ title: '代码审查', status: '待开始', priority: '中', category: '开发', progress: 0 },
{ title: '用户调研', status: '已完成', priority: '低', category: '设计', progress: 100 }
]
这里我们创建了一个包含六个任务的数组,每个任务都包含名称、状态、优先级、分类和进度。
4. 状态管理
为了实现任务筛选功能,我们需要定义一个状态变量来跟踪当前选择的筛选条件:
@State currentFilter: string = '全部'
这个状态变量将用于存储当前选择的任务分类,初始值为"全部",表示显示所有任务。
5. 整体布局结构
任务管理看板的整体布局采用Column容器,内部包含三个主要部分:
build() {
Column() {
// 标题和筛选
Row() {
// ...
}
.margin({ bottom: 16 })
.width('100%')
// 表头
GridRow({ columns: 1 }) {
// ...
}
// 任务列表
Scroll() {
GridRow({ columns: 1 }) {
// ...
}
}
.height('70%')
.margin({ top: 8 })
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.padding(16)
}
这种结构将看板界面分为三个垂直排列的部分:
- 顶部的标题和筛选区域
- 中间的表头区域
- 底部的任务列表区域(可滚动)
整个Column容器设置宽高为100%,内边距为16像素,使内容与屏幕边缘保持适当距离。
6. 标题和筛选功能实现
标题和筛选区域使用Row容器,左侧显示标题,右侧是分类筛选下拉框:
// 标题和筛选
Row() {
Text('任务看板')
.fontSize(20)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.layoutWeight(1)
Select([
{ value: '全部', icon: $r('app.media.01') },
{ value: '设计', icon: $r('app.media.02') },
{ value: '开发', icon: $r('app.media.03') },
{ value: '测试', icon: $r('app.media.04') }
])
.selected(0)
.onSelect((index: number) => {
this.currentFilter = ['全部', '设计', '开发', '测试'][index]
})
.width(120)
}
.margin({ bottom: 16 })
.width('100%')
在这个部分:
- 左侧Text显示"任务看板"标题,设置字体大小为20像素,粗体,并使用layoutWeight(1)使其占据剩余空间
- 右侧Select组件作为分类筛选下拉框,包含四个选项:"全部"、"设计"、"开发"和"测试",每个选项都有对应的图标
- 下拉框初始选中第一项("全部"),宽度为120像素
- onSelect事件处理器在用户选择不同选项时更新currentFilter状态变量
- 整个Row设置下边距为16像素,宽度为100%
7. 表头实现
表头区域使用单列的GridRow和GridCol,内部包含一个Row容器,显示各列的标题:
// 表头
GridRow({ columns: 1 }) {
GridCol({ span: 1 }) {
Row() {
Text('任务名称')
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.width('40%')
Text('状态')
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.width('15%')
Text('优先级')
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.width('15%')
Text('进度')
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.width('30%')
}
.padding(12)
.backgroundColor('#F5F5F5')
.borderRadius(8)
}
}
在这个部分:
- GridRow设置为单列布局(
columns: 1),GridCol占据整个行宽(span: 1) - 内部Row容器包含四个Text组件,分别显示"任务名称"、"状态"、"优先级"和"进度"列标题
- 每个Text组件设置字体大小为14像素,粗体,并设置不同的宽度百分比,使各列按比例分配空间
- 整个Row设置内边距为12像素,背景色为浅灰色(#F5F5F5),边框圆角为8像素
8. 任务列表实现
任务列表区域使用Scroll容器包裹单列的GridRow,通过ForEach循环遍历筛选后的任务数组:
// 任务列表
Scroll() {
GridRow({ columns: 1 }) {
ForEach(this.tasks.filter(task =>
this.currentFilter === '全部' || task.category === this.currentFilter
), (task: TaskType) => {
GridCol({ span: 1 }) {
Row() {
Text(task.title)
.fontSize(14)
.width('40%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Start)
Text(task.status)
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor(this.getStatusColor(task.status))
.width('15%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
Text(task.priority)
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor(this.getPriorityColor(task.priority))
.width('15%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
Progress({ value: task.progress, total: 100, type: ProgressType.Linear })
.width('30%')
.height(8)
.color('#4CAF50')
}
.padding(12)
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFF')
.borderRadius(8)
.margin({ bottom: 8 })
}
})
}
}
.height('70%')
.margin({ top: 8 })
在这个部分:
- Scroll容器使任务列表可滚动,设置高度为父容器的70%,顶部边距为8像素
- 内部GridRow设置为单列布局(
columns: 1) - ForEach循环遍历经过筛选的任务数组,筛选条件是:当前筛选为"全部"或任务分类与当前筛选相匹配
- 每个任务项使用GridCol包裹,占据整个行宽(
span: 1) - 每个任务项内部使用Row容器,包含四个组件,分别显示任务名称、状态、优先级和进度
- 任务名称使用Text组件,宽度为40%,左对齐
- 状态使用Text组件,宽度为15%,居中对齐,文本颜色根据状态动态设置
- 优先级使用Text组件,宽度为15%,居中对齐,文本颜色根据优先级动态设置
- 进度使用Progress组件,宽度为30%,高度为8像素,颜色为绿色
- 整个Row设置内边距为12像素,背景色为白色,边框圆角为8像素,底部边距为8像素
9. 辅助方法实现
为了根据任务状态和优先级设置不同的颜色,我们实现了两个辅助方法:
private getStatusColor(status: string): string {
switch (status) {
case '已完成': return '#4CAF50'
case '进行中': return '#2196F3'
case '待开始': return '#9E9E9E'
default: return '#000000'
}
}
private getPriorityColor(priority: string): string {
switch (priority) {
case '高': return '#F44336'
case '中': return '#FF9800'
case '低': return '#4CAF50'
default: return '#000000'
}
}
这些方法根据任务的状态和优先级返回不同的颜色代码:
- 状态颜色:已完成(绿色)、进行中(蓝色)、待开始(灰色)
- 优先级颜色:高(红色)、中(橙色)、低(绿色)
这种颜色编码使用户可以通过颜色快速识别任务的状态和优先级。
10. 完整代码
下面是任务管理看板网格布局的完整代码:
// 任务管理看板网格布局
interface TaskType {
title: string;
status: string;
priority: string;
category: string;
progress: number;
}
@Component
export struct TaskBoardGrid {
private tasks: TaskType[] = [
{ title: '完成UI设计', status: '进行中', priority: '高', category: '设计', progress: 60 },
{ title: '编写API文档', status: '待开始', priority: '中', category: '开发', progress: 0 },
{ title: '测试登录功能', status: '已完成', priority: '低', category: '测试', progress: 100 },
{ title: '准备会议材料', status: '进行中', priority: '高', category: '管理', progress: 30 },
{ title: '代码审查', status: '待开始', priority: '中', category: '开发', progress: 0 },
{ title: '用户调研', status: '已完成', priority: '低', category: '设计', progress: 100 }
]
@State currentFilter: string = '全部'
build() {
Column() {
// 标题和筛选
Row() {
Text('任务看板')
.fontSize(20)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.layoutWeight(1)
Select([
{ value: '全部', icon: $r('app.media.01') },
{ value: '设计', icon: $r('app.media.02') },
{ value: '开发', icon: $r('app.media.03') },
{ value: '测试', icon: $r('app.media.04') }
])
.selected(0)
.onSelect((index: number) => {
this.currentFilter = ['全部', '设计', '开发', '测试'][index]
})
.width(120)
}
.margin({ bottom: 16 })
.width('100%')
// 表头
GridRow({ columns: 1 }) {
GridCol({ span: 1 }) {
Row() {
Text('任务名称')
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.width('40%')
Text('状态')
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.width('15%')
Text('优先级')
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.width('15%')
Text('进度')
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.width('30%')
}
.padding(12)
.backgroundColor('#F5F5F5')
.borderRadius(8)
}
}
// 任务列表
Scroll() {
GridRow({ columns: 1 }) {
ForEach(this.tasks.filter(task =>
this.currentFilter === '全部' || task.category === this.currentFilter
), (task: TaskType) => {
GridCol({ span: 1 }) {
Row() {
Text(task.title)
.fontSize(14)
.width('40%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Start)
Text(task.status)
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor(this.getStatusColor(task.status))
.width('15%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
Text(task.priority)
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor(this.getPriorityColor(task.priority))
.width('15%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
Progress({ value: task.progress, total: 100, type: ProgressType.Linear })
.width('30%')
.height(8)
.color('#4CAF50')
}
.padding(12)
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFF')
.borderRadius(8)
.margin({ bottom: 8 })
}
})
}
}
.height('70%')
.margin({ top: 8 })
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.padding(16)
}
private getStatusColor(status: string): string {
switch (status) {
case '已完成': return '#4CAF50'
case '进行中': return '#2196F3'
case '待开始': return '#9E9E9E'
default: return '#000000'
}
}
private getPriorityColor(priority: string): string {
switch (priority) {
case '高': return '#F44336'
case '中': return '#FF9800'
case '低': return '#4CAF50'
default: return '#000000'
}
}
}
11. GridRow和GridCol组件详解
在本案例中,我们使用了单列的GridRow和GridCol组件来实现表头和任务列表的布局:
GridRow({ columns: 1 }) {
GridCol({ span: 1 }) {
// 内容
}
}
这种配置使内容在水平方向上占据整个可用宽度,适合用于列表式布局。
11.1 GridRow组件
GridRow是HarmonyOS NEXT提供的网格行容器组件,用于创建网格布局。它具有以下主要属性:
| 属性 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| columns | number | { xs?: number, sm?: number, md?: number, lg?: number, xl?: number, xxl?: number } | 设置布局列数 |
| gutter | number | { x?: number, y?: number } | 栅格间隔 |
| breakpoints | { value: string[], reference: BreakpointsReference } | 设置断点值的断点数列以及基于窗口或容器尺寸的相应参照 |
| direction | GridRowDirection | 栅格布局排列方向 |
11.2 GridCol组件
GridCol是HarmonyOS NEXT提供的网格列容器组件,用于在GridRow中创建网格列。它具有以下主要属性:
| 属性 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| span | number | { xs?: number, sm?: number, md?: number, lg?: number, xl?: number, xxl?: number } | 列宽度 |
| offset | number | { xs?: number, sm?: number, md?: number, lg?: number, xl?: number, xxl?: number } | 列偏移量 |
| order | number | { xs?: number, sm?: number, md?: number, lg?: number, xl?: number, xxl?: number } | 列顺序 |
12. 布局效果分析
本案例中的任务管理看板布局具有以下特点:
- 垂直分区明确:整体布局分为三个垂直区域(标题和筛选、表头、任务列表),结构清晰
- 水平对齐一致:表头和任务项的各列宽度保持一致,使内容垂直对齐
- 视觉区分明显:通过不同的颜色标识任务状态和优先级,提高信息的可读性
- 交互功能实用:通过筛选下拉框可以按分类筛选任务,提高用户体验
- 滚动区域合理:任务列表区域可滚动,适合显示大量任务
这种布局设计使任务管理看板界面既美观又实用,用户可以轻松地查看和筛选任务信息。
13. 总结
本教程详细讲解了如何使用HarmonyOS NEXT的GridRow和GridCol组件实现任务管理看板的网格布局。通过合理的数据结构设计和布局规划,我们创建了一个功能完整、界面美观的任务管理看板。
主要内容包括:
- 任务数据结构设计和数据准备
- 整体布局结构的实现
- 标题和筛选功能的详细实现
- 表头和任务列表的设计与实现
- 状态和优先级的视觉区分
通过本教程,你应该已经掌握了如何使用GridRow和GridCol组件实现列表式布局,以及如何结合其他组件(如Select、Scroll、Progress等)创建功能丰富的界面。这些技能可以应用到各种需要列表展示和数据筛选的场景中,如任务管理、数据分析、信息展示等。
在下一篇教程中,我们将进一步探讨如何优化任务管理看板,添加更多功能和交互效果,使其更加实用和吸引人。
- 0回答
- 5粉丝
- 0关注
