168.[HarmonyOS NEXT 实战案例四:Grid] 可滚动网格布局高级篇
[HarmonyOS NEXT 实战案例四:Grid] 可滚动网格布局高级篇
项目已开源,开源地址: https://gitcode.com/nutpi/HarmonyosNextCaseStudyTutorial , 欢迎fork & star
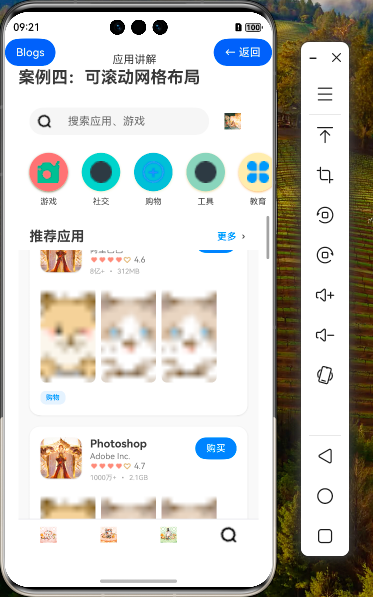
效果演示
1. 引言
在前两篇教程中,我们分别介绍了HarmonyOS NEXT中可滚动网格布局的基础知识和进阶技巧。本篇教程将深入探讨可滚动网格布局的高级应用,包括复杂布局案例、高级交互技术、自定义网格布局算法等内容,帮助开发者掌握Grid组件的高级用法,构建出更加专业、精美的应用界面。
2. 复杂布局案例解析
2.1 应用商店首页布局分析
在我们的示例代码中,实现了一个类似应用商店的首页布局。下面我们对这个复杂布局进行深入分析:
build() {
Column() {
// 顶部搜索栏
this.SearchBar()
// 主要内容区域
Scroll(this.scroller) {
Column() {
// 应用分类标签栏
this.CategoryTabs()
// 推荐应用标题
this.FeaturedAppsTitle()
// 推荐应用网格
Grid(this.scroller) {
ForEach(this.featuredApps, (app: FeaturedApp) => {
GridItem() {
// 应用卡片内容
this.AppCard(app)
}
})
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr')
.rowsGap(16)
.width('100%')
.layoutWeight(1)
.padding({ left: 16, right: 16 })
.backgroundColor('#F5F5F5')
.onScrollIndex((first: number) => {
console.info('first visible item index: ' + first)
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.scrollBar(BarState.Off)
.scrollable(ScrollDirection.Vertical)
// 底部导航栏
this.BottomNavBar()
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor('#F5F5F5')
}
这个布局由以下几个主要部分组成:
- 顶部搜索栏:固定在页面顶部,提供搜索功能
- 主要内容区域:使用Scroll组件实现垂直滚动
- 应用分类标签栏:显示不同的应用分类
- 推荐应用标题:显示推荐应用的标题
- 推荐应用网格:使用Grid组件显示推荐应用列表
- 底部导航栏:固定在页面底部,提供导航功能
这种布局结构非常适合内容丰富的应用首页,既提供了良好的内容组织,又保证了良好的用户体验。
2.2 嵌套滚动结构
在我们的示例中,使用了嵌套的滚动结构:外层是Scroll组件,内层是Grid组件。这种结构有以下优点:
- 灵活的布局控制:外层Scroll负责整体页面的滚动,内层Grid负责网格内容的布局
- 统一的滚动体验:通过共享同一个scroller控制器,确保滚动行为的一致性
- 复杂内容的组织:可以在网格之外添加其他内容,如标题、标签栏等
实现这种嵌套滚动结构的关键是正确设置和共享scroller控制器:
// 创建滚动控制器
private scroller: Scroller = new Scroller()
// 在Scroll和Grid中共享同一个控制器
Scroll(this.scroller) {
// 内容
}
Grid(this.scroller) {
// 网格内容
}
通过这种方式,我们可以实现复杂的嵌套滚动结构,同时保持良好的滚动体验。
2.3 混合布局策略
在复杂应用中,我们通常需要混合使用多种布局组件。以下是一个更复杂的混合布局示例:
Scroll(this.scroller) {
Column() {
// 轮播图部分
Swiper() {
ForEach(this.banners, (banner) => {
Image(banner.image)
.width('100%')
.height(200)
.borderRadius(16)
})
}
.width('100%')
.height(200)
.margin({ top: 16, bottom: 16 })
.autoPlay(true)
// 应用分类标签栏
this.CategoryTabs()
// 热门应用部分 - 水平滚动列表
Text('热门应用')
.fontSize(20)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.margin({ top: 16, bottom: 8 })
Scroll() {
Row() {
ForEach(this.popularApps, (app) => {
this.PopularAppCard(app)
})
}
}
.scrollable(ScrollDirection.Horizontal)
.scrollBar(BarState.Off)
.width('100%')
.height(150)
// 推荐应用标题
this.FeaturedAppsTitle()
// 推荐应用网格
Grid(this.scroller) {
ForEach(this.featuredApps, (app: FeaturedApp) => {
GridItem() {
this.AppCard(app)
}
})
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr')
.rowsGap(16)
.width('100%')
.layoutWeight(1)
}
}
这个示例展示了如何在一个页面中混合使用多种布局组件:
- Swiper:用于显示轮播图
- 水平Scroll:用于显示热门应用的水平滚动列表
- Grid:用于显示推荐应用的网格布局
通过这种混合布局策略,我们可以创建出更加丰富、多样的用户界面。
3. 高级网格项设计
3.1 复杂网格项结构
在我们的示例中,每个应用卡片都是一个复杂的网格项,包含多种信息和交互元素:
@Builder AppCard(app: FeaturedApp) {
Column() {
// 应用图标和基本信息
Row() {
Image(app.icon)
.width(64)
.height(64)
.borderRadius(16)
Column() {
Text(app.name)
.fontSize(16)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
Text(app.developer)
.fontSize(14)
.opacity(0.6)
// 星级评分
this.StarRating(app.rating)
// 下载量和大小
Row() {
Text(app.downloads)
.fontSize(12)
.opacity(0.6)
Text(' • ')
.fontSize(12)
.opacity(0.6)
Text(app.size)
.fontSize(12)
.opacity(0.6)
}
}
.layoutWeight(1)
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Start)
.margin({ left: 16 })
// 获取/购买按钮
Button(app.price === 'Free' ? 'GET' : app.price)
.height(32)
.fontSize(14)
.borderRadius(16)
.backgroundColor(app.price === 'Free' ? '#0A59F7' : '#FFFFFF')
.fontColor(app.price === 'Free' ? '#FFFFFF' : '#0A59F7')
}
.width('100%')
.padding(16)
// 应用截图
Scroll() {
Row() {
ForEach(app.screenshots, (screenshot) => {
Image(screenshot)
.width(240)
.height(160)
.borderRadius(8)
.margin({ right: 8 })
})
}
}
.scrollable(ScrollDirection.Horizontal)
.scrollBar(BarState.Off)
.width('100%')
// 分类标签
Row() {
ForEach(app.categories, (category) => {
Text(category)
.fontSize(12)
.backgroundColor('#F0F0F0')
.borderRadius(12)
.padding({ left: 8, right: 8, top: 4, bottom: 4 })
.margin({ right: 8 })
})
}
.width('100%')
.padding({ left: 16, right: 16, bottom: 16 })
}
.width('100%')
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFF')
.borderRadius(16)
}
这个网格项包含以下元素:
- 应用图标和基本信息:包括图标、名称、开发者、评分、下载量和大小
- 获取/购买按钮:根据应用是免费还是付费显示不同的按钮
- 应用截图:使用水平滚动的Scroll组件显示多张应用截图
- 分类标签:显示应用所属的分类
这种复杂的网格项设计可以在有限的空间内展示丰富的信息,提升用户体验。
3.2 自定义构建器的高级应用
在我们的示例中,使用了自定义构建器来创建可复用的UI组件,如星级评分:
@Builder StarRating(rating: number) {
Row() {
ForEach([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], (star) => {
Image(star <= rating ? '/images/star_filled.png' : '/images/star_empty.png')
.width(16)
.height(16)
.margin({ right: 4 })
})
Text(rating.toFixed(1))
.fontSize(14)
.opacity(0.6)
.margin({ left: 4 })
}
.margin({ top: 4, bottom: 4 })
}
自定义构建器的高级应用包括:
- 参数化构建器:通过传递参数来控制构建器的输出
- 条件渲染:根据条件显示不同的UI元素
- 组合构建器:在一个构建器中使用其他构建器
以下是一个更复杂的自定义构建器示例:
@Builder AppCardVariant(app: FeaturedApp, variant: string = 'default', onAction?: (app: FeaturedApp, action: string) => void) {
// 根据变体类型显示不同的卡片样式
if (variant === 'compact') {
// 紧凑型卡片
Row() {
Image(app.icon)
.width(48)
.height(48)
.borderRadius(12)
Column() {
Text(app.name)
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
this.StarRating(app.rating)
}
.layoutWeight(1)
.margin({ left: 12 })
Button('GET')
.height(28)
.fontSize(12)
.borderRadius(14)
.onClick(() => {
onAction?.(app, 'download')
})
}
.width('100%')
.padding(12)
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFF')
.borderRadius(12)
} else if (variant === 'featured') {
// 特色卡片
Column() {
Image(app.screenshots[0])
.width('100%')
.height(200)
.borderRadius({ topLeft: 16, topRight: 16 })
Row() {
Image(app.icon)
.width(56)
.height(56)
.borderRadius(12)
.margin({ top: -28 })
Column() {
Text(app.name)
.fontSize(16)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
Text(app.developer)
.fontSize(14)
.opacity(0.6)
}
.layoutWeight(1)
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Start)
.margin({ left: 12 })
Button('GET')
.height(32)
.fontSize(14)
.borderRadius(16)
.onClick(() => {
onAction?.(app, 'download')
})
}
.width('100%')
.padding(16)
this.StarRating(app.rating)
.margin({ left: 16, bottom: 16 })
}
.width('100%')
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFF')
.borderRadius(16)
} else {
// 默认卡片
this.AppCard(app)
}
}
这个高级构建器根据传入的变体类型显示不同样式的应用卡片,并支持自定义操作回调,展示了自定义构建器的强大功能。
3.3 动态内容与条件渲染
在复杂的网格项中,我们通常需要根据数据动态渲染内容。以下是一些高级的动态内容和条件渲染技巧:
@Builder AppCard(app: FeaturedApp) {
Column() {
// 基本信息
// ...
// 条件渲染:只有当有截图时才显示截图部分
if (app.screenshots && app.screenshots.length > 0) {
Scroll() {
Row() {
ForEach(app.screenshots, (screenshot) => {
Image(screenshot)
.width(240)
.height(160)
.borderRadius(8)
.margin({ right: 8 })
})
}
}
.scrollable(ScrollDirection.Horizontal)
.scrollBar(BarState.Off)
.width('100%')
}
// 动态内容:根据应用类型显示不同的标签
Row() {
if (app.isEditor) {
Text('编辑推荐')
.fontSize(12)
.fontColor('#FF6B22')
.backgroundColor('#FFF0E6')
.borderRadius(12)
.padding({ left: 8, right: 8, top: 4, bottom: 4 })
.margin({ right: 8 })
}
if (app.isNew) {
Text('新上架')
.fontSize(12)
.fontColor('#14B37D')
.backgroundColor('#E6F9F1')
.borderRadius(12)
.padding({ left: 8, right: 8, top: 4, bottom: 4 })
.margin({ right: 8 })
}
// 分类标签
ForEach(app.categories, (category) => {
Text(category)
.fontSize(12)
.backgroundColor('#F0F0F0')
.borderRadius(12)
.padding({ left: 8, right: 8, top: 4, bottom: 4 })
.margin({ right: 8 })
})
}
.width('100%')
.padding({ left: 16, right: 16, bottom: 16 })
// 条件渲染:只有付费应用才显示应用内购买信息
if (app.price !== 'Free' && app.inAppPurchases) {
Text('包含应用内购买项目')
.fontSize(12)
.opacity(0.6)
.width('100%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.padding({ bottom: 16 })
}
}
}
这个示例展示了如何根据应用数据动态渲染不同的内容,包括:
- 条件显示截图:只有当应用有截图时才显示截图部分
- 动态标签:根据应用属性显示不同的标签,如"编辑推荐"、"新上架"等
- 条件显示购买信息:只有付费应用才显示应用内购买信息
通过这些技巧,我们可以创建出更加智能、动态的网格项,提升用户体验。
4. 高级交互与动画
4.1 滚动驱动动画
滚动驱动动画是一种高级的交互效果,可以根据滚动位置动态调整UI元素的属性。以下是一个实现滚动驱动动画的示例:
// 创建滚动控制器
private scroller: Scroller = new Scroller()
// 滚动位置状态
@State scrollY: number = 0
// 监听滚动事件
onPageShow() {
this.scroller.scrollTo({
xOffset: 0,
yOffset: 0
})
// 添加滚动监听
this.scroller.onScroll((offset: { xOffset: number, yOffset: number }) => {
this.scrollY = offset.yOffset
})
}
build() {
Stack() {
// 主要内容
Scroll(this.scroller) {
// 内容
}
// 顶部搜索栏 - 滚动驱动动画
Row() {
// 搜索栏内容
}
.width('100%')
.height(56)
.padding({ left: 16, right: 16 })
.backgroundColor(Color.lerp(new Color('#FFFFFF00'), new Color('#FFFFFFFF'), Math.min(this.scrollY / 100, 1)))
.shadow({
radius: 8,
color: Color.lerp(new Color('#00000000'), new Color('#00000022'), Math.min(this.scrollY / 100, 1)),
offsetY: 2
})
}
}
这个示例实现了一个滚动时渐变的顶部搜索栏:
- 当页面滚动到顶部时,搜索栏是透明的
- 随着页面向下滚动,搜索栏逐渐变为白色背景并显示阴影
- 使用Color.lerp函数根据滚动位置计算颜色和阴影的插值
这种滚动驱动动画可以创造出更加流畅、自然的交互体验。
4.2 视差滚动效果
视差滚动是一种高级的滚动效果,可以使不同层次的元素以不同的速度滚动,创造出深度感。以下是一个实现视差滚动的示例:
@State scrollY: number = 0
build() {
Stack() {
// 背景层 - 慢速滚动
Image('/images/background.png')
.width('100%')
.height('120%')
.objectFit(ImageFit.Cover)
.translate({ y: -this.scrollY * 0.3 }) // 慢速滚动
// 中间层 - 中速滚动
Image('/images/middle_layer.png')
.width('100%')
.height('110%')
.objectFit(ImageFit.Cover)
.translate({ y: -this.scrollY * 0.6 }) // 中速滚动
// 前景层 - 正常滚动
Scroll(this.scroller) {
Column() {
// 内容
}
.height(2000) // 确保有足够的滚动空间
}
.scrollBar(BarState.Off)
.onScroll((offset: { xOffset: number, yOffset: number }) => {
this.scrollY = offset.yOffset
})
}
}
这个示例创建了三层视差滚动效果:
- 背景层:以0.3倍的速度滚动,创造出远处的效果
- 中间层:以0.6倍的速度滚动,创造出中等距离的效果
- 前景层:以正常速度滚动,包含主要内容
通过这种视差滚动效果,可以为应用添加深度感和立体感,提升视觉体验。
4.3 高级手势交互
结合Grid和手势,我们可以实现更加复杂的交互效果。以下是一个实现网格项缩放和旋转效果的示例:
@State gestureX: number = 0
@State gestureY: number = 0
@State scale: number = 1.0
@State rotation: number = 0
GridItem() {
Column() {
// 网格项内容
}
.scale({ x: this.scale, y: this.scale })
.rotate({ angle: this.rotation })
.translate({ x: this.gestureX, y: this.gestureY })
.gesture(
GestureGroup(GestureMode.Parallel,
PinchGesture()
.onActionUpdate((event: GestureEvent) => {
this.scale = Math.max(0.5, Math.min(2.0, this.scale * event.scale))
})
.onActionEnd(() => {
// 缩放结束后恢复正常大小
animateTo({ duration: 300, curve: Curve.Ease }, () => {
this.scale = 1.0
})
}),
RotationGesture()
.onActionUpdate((event: GestureEvent) => {
this.rotation += event.angle
})
.onActionEnd(() => {
// 旋转结束后恢复正常角度
animateTo({ duration: 300, curve: Curve.Ease }, () => {
this.rotation = 0
})
}),
PanGesture()
.onActionUpdate((event: GestureEvent) => {
this.gestureX += event.offsetX
this.gestureY += event.offsetY
})
.onActionEnd(() => {
// 拖拽结束后恢复正常位置
animateTo({ duration: 300, curve: Curve.Ease }, () => {
this.gestureX = 0
this.gestureY = 0
})
})
)
)
}
这个示例实现了三种手势交互:
- 捏合手势:用于缩放网格项
- 旋转手势:用于旋转网格项
- 拖拽手势:用于移动网格项
所有手势结束后,网格项会通过动画恢复到正常状态。这种高级手势交互可以为应用添加更加丰富、自然的交互体验。
5. 高级布局算法与自定义
5.1 自定义网格布局算法
在某些特殊场景下,Grid组件的默认布局可能无法满足需求。这时,我们可以实现自定义的网格布局算法:
// 自定义瀑布流布局
class WaterfallLayout {
private columnHeights: number[] = []
private columnCount: number = 2
private itemPositions: Map<number, { x: number, y: number }> = new Map()
constructor(columnCount: number = 2) {
this.columnCount = columnCount
this.resetLayout()
}
resetLayout() {
this.columnHeights = new Array(this.columnCount).fill(0)
this.itemPositions.clear()
}
// 计算项目位置
calculateItemPosition(itemId: number, itemHeight: number) {
// 找出高度最小的列
let minColumnIndex = 0
let minHeight = this.columnHeights[0]
for (let i = 1; i < this.columnCount; i++) {
if (this.columnHeights[i] < minHeight) {
minHeight = this.columnHeights[i]
minColumnIndex = i
}
}
// 计算位置
const columnWidth = 100 / this.columnCount
const x = minColumnIndex * columnWidth
const y = this.columnHeights[minColumnIndex]
// 更新列高度
this.columnHeights[minColumnIndex] += itemHeight + 16 // 16是间距
// 保存位置
this.itemPositions.set(itemId, { x, y })
return { x: `${x}%`, y: y }
}
getItemPosition(itemId: number) {
return this.itemPositions.get(itemId)
}
getContentHeight() {
return Math.max(...this.columnHeights)
}
}
// 使用自定义布局
@State waterfallLayout: WaterfallLayout = new WaterfallLayout(2)
@State itemHeights: Map<number, number> = new Map()
aboutToAppear() {
// 预设项目高度(实际应用中可能需要动态计算)
this.featuredApps.forEach((app, index) => {
// 模拟不同高度的项目
const height = 200 + Math.random() * 200
this.itemHeights.set(app.id, height)
})
// 计算初始布局
this.waterfallLayout.resetLayout()
this.featuredApps.forEach(app => {
this.waterfallLayout.calculateItemPosition(app.id, this.itemHeights.get(app.id) || 200)
})
}
build() {
Column() {
// 其他内容
// 自定义瀑布流布局
Stack() {
ForEach(this.featuredApps, (app: FeaturedApp) => {
Column() {
// 应用卡片内容
this.AppCard(app)
}
.width(`${100 / this.waterfallLayout.columnCount}%`)
.height(this.itemHeights.get(app.id) || 200)
.position({
x: this.waterfallLayout.getItemPosition(app.id)?.x || '0%',
y: this.waterfallLayout.getItemPosition(app.id)?.y || 0
})
})
}
.width('100%')
.height(this.waterfallLayout.getContentHeight())
.margin({ top: 16 })
}
}
这个示例实现了一个自定义的瀑布流布局算法:
- WaterfallLayout类:负责计算每个项目的位置
- 跟踪每列的当前高度
- 为新项目选择高度最小的列
- 计算并存储每个项目的位置
- 布局应用:
- 预设每个项目的高度(实际应用中可能需要动态计算)
- 使用Stack组件和绝对定位实现自定义布局
- 根据计算的位置放置每个项目
通过这种方式,我们可以实现Grid组件无法直接支持的复杂布局,如瀑布流布局。
5.2 动态网格布局
在某些场景下,我们需要根据内容动态调整网格布局。以下是一个实现动态网格布局的示例:
@State gridItems: Array<{
id: number,
content: string,
rowSpan: number,
columnSpan: number
}> = []
aboutToAppear() {
// 生成动态网格项
this.generateGridItems()
}
generateGridItems() {
const items = []
let id = 0
// 添加一个大项目(跨2行2列)
items.push({
id: id++,
content: '特色内容',
rowSpan: 2,
columnSpan: 2
})
// 添加4个普通项目
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
items.push({
id: id++,
content: `内容 ${i + 1}`,
rowSpan: 1,
columnSpan: 1
})
}
// 添加一个宽项目(跨2列)
items.push({
id: id++,
content: '宽内容',
rowSpan: 1,
columnSpan: 2
})
// 添加更多普通项目
for (let i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
items.push({
id: id++,
content: `内容 ${i + 5}`,
rowSpan: 1,
columnSpan: 1
})
}
this.gridItems = items
}
build() {
Column() {
// 动态网格布局
Grid() {
ForEach(this.gridItems, (item) => {
GridItem() {
Text(item.content)
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.backgroundColor('#F0F0F0')
.borderRadius(8)
}
.rowStart(0) // 自动布局
.rowEnd(0)
.columnStart(0)
.columnEnd(0)
// 设置跨行跨列
.forceRebuild(true)
.gridSpan({
rowSpan: item.rowSpan,
columnSpan: item.columnSpan
})
})
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
.columnsGap(16)
.rowsGap(16)
.width('100%')
.height(600)
}
}
这个示例实现了一个动态网格布局:
- 动态生成网格项:包括不同大小的项目(普通项目、大项目、宽项目)
- 设置跨行跨列:使用gridSpan属性设置每个项目的跨行跨列
- 自动布局:将rowStart、rowEnd、columnStart、columnEnd设置为0,让Grid自动布局
通过这种方式,我们可以创建出更加灵活、动态的网格布局。
6. 总结
本教程深入探讨了HarmonyOS NEXT中可滚动网格布局的高级应用,包括复杂布局案例解析、高级网格项设计、高级交互与动画、高级布局算法与自定义等内容。通过这些高级技巧,开发者可以构建出更加专业、精美、交互丰富的应用界面。
- 0回答
- 5粉丝
- 0关注
