171.[HarmonyOS NEXT 实战案例五:Grid] 动态网格布局高级篇
[HarmonyOS NEXT 实战案例五:Grid] 动态网格布局高级篇
项目已开源,开源地址: https://gitcode.com/nutpi/HarmonyosNextCaseStudyTutorial , 欢迎fork & star
效果演示
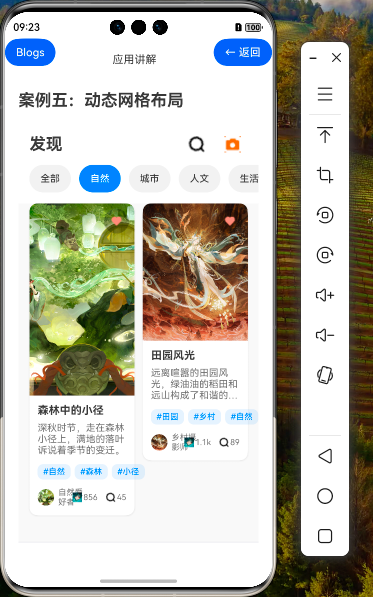 在前两篇教程中,我们学习了动态网格布局的基础知识和进阶技巧。本篇教程将深入探讨动态网格布局的高级应用,包括复杂交互场景、自定义布局算法、性能优化策略等内容,帮助你掌握构建专业级瀑布流界面的技能。
在前两篇教程中,我们学习了动态网格布局的基础知识和进阶技巧。本篇教程将深入探讨动态网格布局的高级应用,包括复杂交互场景、自定义布局算法、性能优化策略等内容,帮助你掌握构建专业级瀑布流界面的技能。
1. 复杂交互场景实现
1.1 拖拽排序
在某些应用中,我们需要允许用户通过拖拽来重新排序网格项。HarmonyOS NEXT提供了手势识别功能,可以实现拖拽排序效果。
首先,我们需要定义一个状态来跟踪拖拽操作:
@State draggingIndex: number = -1 // -1表示没有拖拽
@State dragPosition: { x: number, y: number } = { x: 0, y: 0 }
@State itemPositions: Array<{ x: number, y: number }> = []
然后,为每个GridItem添加拖拽手势:
GridItem() {
PhotoCard(item)
.gesture(
PanGesture({ fingers: 1, direction: PanDirection.All })
.onActionStart((event: GestureEvent) => {
this.draggingIndex = index
this.dragPosition = { x: event.offsetX, y: event.offsetY }
})
.onActionUpdate((event: GestureEvent) => {
this.dragPosition = { x: event.offsetX, y: event.offsetY }
this.updateDragPosition()
})
.onActionEnd(() => {
this.finalizeDragOperation()
this.draggingIndex = -1
})
)
.zIndex(this.draggingIndex === index ? 10 : 1)
.position({
x: this.draggingIndex === index ? this.dragPosition.x : this.itemPositions[index]?.x || 0,
y: this.draggingIndex === index ? this.dragPosition.y : this.itemPositions[index]?.y || 0
})
.animation({
duration: this.draggingIndex === index ? 0 : 300,
curve: Curve.EaseOut
})
}
最后,实现拖拽位置更新和排序逻辑:
updateDragPosition() {
if (this.draggingIndex < 0) return
// 计算当前拖拽项与其他项的位置关系
// 确定是否需要交换位置
const dragItem = this.photoItems[this.draggingIndex]
const dragRect = {
x: this.dragPosition.x,
y: this.dragPosition.y,
width: this.getItemWidth(),
height: dragItem.height
}
for (let i = 0; i < this.photoItems.length; i++) {
if (i === this.draggingIndex) continue
const itemRect = {
x: this.itemPositions[i].x,
y: this.itemPositions[i].y,
width: this.getItemWidth(),
height: this.photoItems[i].height
}
// 检测碰撞
if (this.isRectOverlap(dragRect, itemRect)) {
// 交换位置
this.swapItems(this.draggingIndex, i)
this.draggingIndex = i
break
}
}
}
finalizeDragOperation() {
// 完成拖拽操作,更新数据顺序
// 可能需要调用API保存新的顺序
}
isRectOverlap(rect1, rect2) {
// 检测两个矩形是否重叠
return !(rect1.x + rect1.width < rect2.x ||
rect2.x + rect2.width < rect1.x ||
rect1.y + rect1.height < rect2.y ||
rect2.y + rect2.height < rect1.y)
}
swapItems(index1, index2) {
// 交换两个项的位置
const temp = this.photoItems[index1]
this.photoItems[index1] = this.photoItems[index2]
this.photoItems[index2] = temp
// 交换位置信息
const tempPos = this.itemPositions[index1]
this.itemPositions[index1] = this.itemPositions[index2]
this.itemPositions[index2] = tempPos
}
1.2 卡片展开/折叠
在瀑布流布局中,我们可能需要实现卡片展开/折叠功能,以显示更多内容。
首先,为每个卡片添加展开状态:
@State expandedItems: Set<number> = new Set()
isExpanded(id: number): boolean {
return this.expandedItems.has(id)
}
toggleExpand(id: number) {
if (this.expandedItems.has(id)) {
this.expandedItems.delete(id)
} else {
this.expandedItems.add(id)
}
}
然后,根据展开状态调整卡片内容:
GridItem() {
Column() {
// 图片部分
// ...
// 内容区域
Column() {
// 标题
Text(item.title)
.fontSize(16)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.fontColor('#333333')
.maxLines(2)
.textOverflow({ overflow: TextOverflow.Ellipsis })
.width('100%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Start)
// 描述
Text(item.description)
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor('#666666')
.maxLines(this.isExpanded(item.id) ? 10 : 3) // 展开时显示更多行
.textOverflow({ overflow: TextOverflow.Ellipsis })
.width('100%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Start)
.margin({ top: 8 })
// 展开/折叠按钮
if (item.description.length > 100) { // 只有长描述才显示按钮
Text(this.isExpanded(item.id) ? '收起' : '展开')
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor('#007AFF')
.margin({ top: 8 })
.onClick(() => {
this.toggleExpand(item.id)
})
}
// 其他内容
// ...
}
.padding(12)
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Start)
}
.height(this.isExpanded(item.id) ? undefined : item.height + 150) // 展开时高度自适应
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFF')
.borderRadius(12)
.animation({
duration: 300,
curve: Curve.EaseOut
})
}
1.3 滑动操作
我们可以为网格项添加滑动操作,例如滑动删除、收藏等功能。
GridItem() {
Swiper() {
// 主内容
PhotoCard(item)
// 操作按钮
Row() {
Button() {
Image($r('app.media.delete_icon'))
.width(24)
.height(24)
.fillColor('#FFFFFF')
}
.width(80)
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor('#FF3B30')
.onClick(() => {
this.deleteItem(item.id)
})
Button() {
Image($r('app.media.star_icon'))
.width(24)
.height(24)
.fillColor('#FFFFFF')
}
.width(80)
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor('#FFCC00')
.onClick(() => {
this.favoriteItem(item.id)
})
}
}
.displayCount(1)
.index(0)
.loop(false)
.duration(300)
.indicator(false)
}
2. 自定义布局算法
2.1 优化瀑布流布局算法
标准的Grid组件可能无法完全满足复杂瀑布流的需求,我们可以实现自定义的瀑布流布局算法。
@State columnHeights: number[] = [] // 每列的当前高度
@State itemLayout: Array<{ column: number, top: number }> = [] // 每个项的布局信息
calculateLayout() {
const columnCount = this.columnsCount
const columnWidth = px2vp(window.getWindowWidth()) / columnCount - 12 // 考虑间距
// 初始化列高度
this.columnHeights = new Array(columnCount).fill(0)
this.itemLayout = []
// 计算每个项的位置
this.photoItems.forEach((item, index) => {
// 找出高度最小的列
let minColumn = 0
for (let i = 1; i < columnCount; i++) {
if (this.columnHeights[i] < this.columnHeights[minColumn]) {
minColumn = i
}
}
// 计算实际高度(根据宽高比)
const aspectRatio = 1 // 假设为1:1,实际应根据图片信息计算
const height = columnWidth / aspectRatio
// 记录布局信息
this.itemLayout[index] = {
column: minColumn,
top: this.columnHeights[minColumn]
}
// 更新列高度
this.columnHeights[minColumn] += height + 16 // 加上间距
})
}
然后,在构建UI时使用这些布局信息:
build() {
Column() {
// 其他UI元素
// 自定义瀑布流
Stack() {
ForEach(this.photoItems, (item: PhotoItems, index) => {
PhotoCard(item)
.position({
x: this.itemLayout[index].column * (this.getItemWidth() + 12),
y: this.itemLayout[index].top
})
.width(this.getItemWidth())
})
}
.width('100%')
.height(Math.max(...this.columnHeights) + 100) // 确保足够高度
}
}
getItemWidth(): number {
return px2vp(window.getWindowWidth()) / this.columnsCount - 12
}
2.2 动态高度计算
为了更准确地计算瀑布流布局,我们需要知道每个图片的实际宽高比。可以通过预加载图片或使用固定的宽高比来实现。
// 预加载图片并获取宽高比
async preloadImages() {
const promises = this.photoItems.map(async (item) => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
const image = new Image()
image.src = item.imageUrl
image.onload = () => {
item.aspectRatio = image.width / image.height
resolve()
}
image.onerror = () => {
item.aspectRatio = 1 // 默认1:1
resolve()
}
})
})
await Promise.all(promises)
this.calculateLayout()
}
2.3 虚拟滚动优化
对于大量数据的瀑布流,可以实现虚拟滚动,只渲染可见区域的项,提高性能。
@State visibleStartIndex: number = 0
@State visibleEndIndex: number = 20 // 初始可见数量
updateVisibleItems(scrollY: number) {
const screenHeight = px2vp(window.getWindowHeight())
const bufferHeight = 500 // 上下缓冲区高度
// 计算可见范围
let startIndex = this.photoItems.length - 1
let endIndex = 0
for (let i = 0; i < this.photoItems.length; i++) {
const itemTop = this.itemLayout[i].top
const itemHeight = this.getItemHeight(i)
const itemBottom = itemTop + itemHeight
// 判断是否在可见范围内(包括缓冲区)
if (itemBottom >= scrollY - bufferHeight && itemTop <= scrollY + screenHeight + bufferHeight) {
startIndex = Math.min(startIndex, i)
endIndex = Math.max(endIndex, i)
}
}
this.visibleStartIndex = startIndex
this.visibleEndIndex = endIndex
}
build() {
Column() {
// 其他UI元素
// 虚拟滚动瀑布流
Stack() {
ForEach(this.photoItems.slice(this.visibleStartIndex, this.visibleEndIndex + 1),
(item: PhotoItems, index) => {
const actualIndex = index + this.visibleStartIndex
PhotoCard(item)
.position({
x: this.itemLayout[actualIndex].column * (this.getItemWidth() + 12),
y: this.itemLayout[actualIndex].top
})
.width(this.getItemWidth())
})
}
.width('100%')
.height(Math.max(...this.columnHeights) + 100)
.onScroll((_, yOffset) => {
this.updateVisibleItems(yOffset)
})
}
}
3. 高级动画效果
3.1 滚动视差效果
我们可以为瀑布流添加滚动视差效果,使界面更加生动。
@State scrollY: number = 0
build() {
Column() {
// 顶部视差背景
Stack() {
Image($r('app.media.header_bg'))
.width('100%')
.height(200)
.objectFit(ImageFit.Cover)
.translate({ y: this.scrollY * 0.5 }) // 背景滚动速度减半
Text('发现')
.fontSize(32)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.fontColor('#FFFFFF')
.opacity(1 - Math.min(this.scrollY / 100, 1)) // 滚动时淡出
.translate({ y: -this.scrollY * 0.2 }) // 标题滚动速度减慢
}
.width('100%')
.height(200 - Math.min(this.scrollY, 150)) // 滚动时缩小高度
.clip(true)
// 瀑布流内容
Grid() {
// GridItems
}
.onScroll((_, yOffset) => {
this.scrollY = yOffset
})
}
}
3.2 项目动画序列
我们可以为网格项添加序列动画,使它们依次显示。
@State animatedItems: Set<number> = new Set()
build() {
Grid() {
ForEach(this.getFilteredPhotos(), (item: PhotoItems, index) => {
GridItem() {
PhotoCard(item)
}
.opacity(this.animatedItems.has(index) ? 1 : 0)
.scale({ x: this.animatedItems.has(index) ? 1 : 0.8, y: this.animatedItems.has(index) ? 1 : 0.8 })
.animation({
duration: 300,
curve: Curve.EaseOut
})
.onAppear(() => {
// 延迟添加动画,创造序列效果
setTimeout(() => {
this.animatedItems.add(index)
}, 50 * index)
})
})
}
}
3.3 交互反馈动画
为用户交互添加反馈动画,提升用户体验。
@State pressedItem: number = -1
build() {
Grid() {
ForEach(this.getFilteredPhotos(), (item: PhotoItems, index) => {
GridItem() {
PhotoCard(item)
}
.scale({ x: this.pressedItem === index ? 0.95 : 1, y: this.pressedItem === index ? 0.95 : 1 })
.animation({ duration: 100 })
.gesture(
LongPressGesture({ repeat: false })
.onAction(() => {
this.showItemOptions(item)
})
)
.onTouch((event) => {
if (event.type === TouchType.Down) {
this.pressedItem = index
} else if (event.type === TouchType.Up || event.type === TouchType.Cancel) {
this.pressedItem = -1
}
})
})
}
}
4. 高级数据处理
4.1 数据分页与缓存
对于大量数据,我们需要实现分页加载和数据缓存机制。
@State currentPage: number = 1
@State pageSize: number = 20
@State totalItems: number = 0
@State cachedPages: Map<number, PhotoItems[]> = new Map()
async loadPage(page: number) {
// 检查缓存
if (this.cachedPages.has(page)) {
if (page === 1) {
this.photoItems = this.cachedPages.get(page)
} else {
this.photoItems = [...this.photoItems, ...this.cachedPages.get(page)]
}
return
}
// 加载新数据
this.loading = true
try {
// 模拟API请求
const response = await this.fetchPhotos(page, this.pageSize)
const newItems = response.items
this.totalItems = response.total
// 更新缓存
this.cachedPages.set(page, newItems)
// 更新显示
if (page === 1) {
this.photoItems = newItems
} else {
this.photoItems = [...this.photoItems, ...newItems]
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to load data:', error)
} finally {
this.loading = false
}
}
async fetchPhotos(page: number, pageSize: number) {
// 模拟网络请求
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
// 生成模拟数据
const items = Array.from({ length: pageSize }, (_, i) => ({
id: (page - 1) * pageSize + i + 1,
imageUrl: $r('app.media.big' + ((page - 1) * pageSize + i) % 30),
title: `图片标题 ${(page - 1) * pageSize + i + 1}`,
author: `作者 ${(page - 1) * pageSize + i + 1}`,
authorAvatar: $r('app.media.big' + ((page - 1) * pageSize + i) % 30),
likes: Math.floor(Math.random() * 5000),
comments: Math.floor(Math.random() * 500),
tags: ['标签1', '标签2', '标签3'].slice(0, Math.floor(Math.random() * 3) + 1),
height: 150 + Math.floor(Math.random() * 200), // 随机高度
isLiked: Math.random() > 0.5,
description: `这是图片 ${(page - 1) * pageSize + i + 1} 的描述文本,描述了图片的内容和背景。`
}))
resolve({
items,
total: 100 // 总数
})
}, 1000)
})
}
4.2 数据预加载
为了提供更流畅的用户体验,我们可以实现数据预加载。
preloadNextPage() {
const nextPage = this.currentPage + 1
if (nextPage * this.pageSize <= this.totalItems && !this.cachedPages.has(nextPage)) {
// 预加载下一页数据但不显示
this.fetchPhotos(nextPage, this.pageSize).then(response => {
this.cachedPages.set(nextPage, response.items)
})
}
}
async loadMore() {
if (this.loading || this.currentPage * this.pageSize >= this.totalItems) return
this.currentPage++
await this.loadPage(this.currentPage)
this.preloadNextPage() // 预加载下一页
}
4.3 数据过滤与排序
实现高级的数据过滤和排序功能。
@State sortBy: string = 'newest' // newest, popular, recommended
@State filterTags: string[] = []
getFilteredAndSortedPhotos(): PhotoItems[] {
let result = [...this.photoItems]
// 应用过滤
if (this.selectedCategory !== '全部') {
result = result.filter(item =>
item.tags.some(tag => tag.includes(this.selectedCategory))
)
}
if (this.filterTags.length > 0) {
result = result.filter(item =>
this.filterTags.some(tag => item.tags.includes(tag))
)
}
if (this.searchKeyword.trim() !== '') {
result = result.filter(item =>
item.title.includes(this.searchKeyword) ||
item.author.includes(this.searchKeyword) ||
item.tags.some(tag => tag.includes(this.searchKeyword))
)
}
// 应用排序
switch (this.sortBy) {
case 'newest':
result.sort((a, b) => b.id - a.id) // 假设id越大越新
break
case 'popular':
result.sort((a, b) => b.likes - a.likes)
break
case 'recommended':
// 自定义推荐算法
result.sort((a, b) => {
const scoreA = a.likes * 0.7 + a.comments * 0.3
const scoreB = b.likes * 0.7 + b.comments * 0.3
return scoreB - scoreA
})
break
}
return result
}
5. 案例解析:社交媒体发现页
现在,让我们将所学知识应用到一个实际案例中:社交媒体的发现页。
5.1 页面结构
build() {
Column() {
// 顶部导航栏
this.buildHeader()
// 分类和筛选栏
if (!this.showSearch) {
this.buildCategoryBar()
}
// 主内容区
Stack() {
// 瀑布流内容
Refresh({ refreshing: $$this.refreshing }) {
this.buildWaterfallGrid()
}
.onRefresh(() => {
this.refreshData()
})
// 加载指示器
if (this.loading && !this.refreshing) {
LoadingProgress()
.width(36)
.height(36)
.color('#007AFF')
}
// 空状态
if (this.getFilteredAndSortedPhotos().length === 0 && !this.loading) {
Column() {
Image($r('app.media.empty_state'))
.width(120)
.height(120)
.margin({ bottom: 16 })
Text('没有找到相关内容')
.fontSize(16)
.fontColor('#999999')
if (this.searchKeyword || this.selectedCategory !== '全部' || this.filterTags.length > 0) {
Button('清除筛选')
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor('#FFFFFF')
.backgroundColor('#007AFF')
.borderRadius(20)
.padding({ left: 16, right: 16, top: 8, bottom: 8 })
.margin({ top: 16 })
.onClick(() => {
this.resetFilters()
})
}
}
.width('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.margin({ top: 100 })
}
}
.layoutWeight(1)
// 底部导航栏
this.buildBottomNav()
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor('#F8F8F8')
}
5.2 瀑布流实现
@Builder
buildWaterfallGrid() {
Grid() {
// 排序选项(跨越所有列)
GridItem() {
Row() {
ForEach(['最新', '热门', '推荐'], (option, index) => {
Text(option)
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor(this.getSortOption() === index ? '#007AFF' : '#666666')
.fontWeight(this.getSortOption() === index ? FontWeight.Bold : FontWeight.Normal)
.padding({ left: 12, right: 12, top: 8, bottom: 8 })
.onClick(() => {
this.setSortOption(index)
})
if (index < 2) {
Divider()
.vertical(true)
.height(16)
.color('#E0E0E0')
}
})
}
.width('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFF')
.borderRadius(20)
.padding({ top: 4, bottom: 4 })
.margin({ bottom: 16 })
}
.columnSpan(this.columnsCount)
// 瀑布流内容
ForEach(this.getFilteredAndSortedPhotos(), (item: PhotoItems, index) => {
GridItem() {
PhotoCard({
item: item,
onLike: () => this.toggleLike(item.id),
onExpand: () => this.toggleExpand(item.id),
isExpanded: this.isExpanded(item.id)
})
}
.opacity(this.animatedItems.has(index) ? 1 : 0)
.scale({ x: this.animatedItems.has(index) ? 1 : 0.9, y: this.animatedItems.has(index) ? 1 : 0.9 })
.animation({
delay: 30 * (index % this.columnsCount),
duration: 300,
curve: Curve.EaseOut
})
.onAppear(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
this.animatedItems.add(index)
}, 50 * Math.floor(index / this.columnsCount))
})
})
// 加载更多指示器
if (this.hasMore && !this.loading) {
GridItem() {
Text('上拉加载更多')
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor('#999999')
.padding(16)
}
.columnSpan(this.columnsCount)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
}
.columnsTemplate(this.getColumnsTemplate())
.rowsGap(16)
.columnsGap(12)
.width('100%')
.padding({ left: 16, right: 16, bottom: 16 })
.onReachEnd(() => {
if (!this.loading && this.hasMore) {
this.loadMore()
}
})
.onScroll((_, yOffset) => {
this.scrollY = yOffset
this.updateHeaderOpacity()
})
}
5.3 性能优化
// 图片懒加载组件
@Component
struct LazyImage {
@Prop src: Resource
@Prop width: string | number
@Prop height: string | number
@State loaded: boolean = false
@State visible: boolean = false
@State error: boolean = false
aboutToAppear() {
// 延迟加载,避免一次性加载过多图片
setTimeout(() => {
this.visible = true
}, Math.random() * 300)
}
build() {
Stack() {
// 占位背景
Rectangle()
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.fill('#F0F0F0')
if (this.visible) {
if (!this.error) {
Image(this.src)
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.objectFit(ImageFit.Cover)
.opacity(this.loaded ? 1 : 0)
.animation({ duration: 300 })
.onComplete(() => {
this.loaded = true
})
.onError(() => {
this.error = true
})
} else {
// 加载失败显示
Column() {
Image($r('app.media.image_error'))
.width(24)
.height(24)
.margin({ bottom: 8 })
Text('加载失败')
.fontSize(12)
.fontColor('#999999')
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
}
// 加载指示器
if (this.visible && !this.loaded && !this.error) {
LoadingProgress()
.width(24)
.height(24)
.color('#CCCCCC')
}
}
.width(this.width)
.height(this.height)
}
}
总结
本教程深入探讨了HarmonyOS NEXT中动态网格布局的高级应用,包括复杂交互场景、自定义布局算法、高级动画效果、数据处理策略等内容。通过这些高级技巧,你可以构建专业级的瀑布流界面,提供流畅、美观、高效的用户体验。
- 0回答
- 5粉丝
- 0关注
