176.[HarmonyOS NEXT 实战案例七:Grid] 嵌套网格布局进阶篇:高级布局与交互技巧
[HarmonyOS NEXT 实战案例七:Grid] 嵌套网格布局进阶篇:高级布局与交互技巧
项目已开源,开源地址: https://gitcode.com/nutpi/HarmonyosNextCaseStudyTutorial , 欢迎fork & star
效果演示
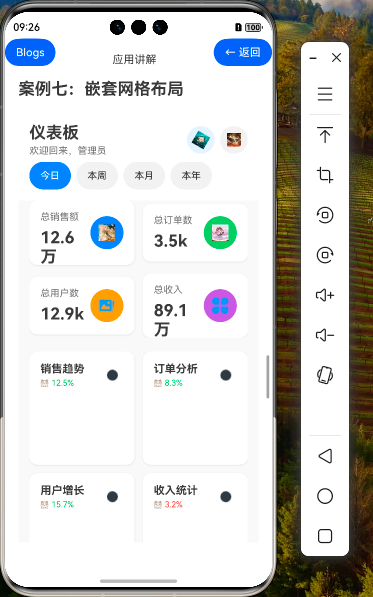
1. 引言
在上一篇教程中,我们介绍了HarmonyOS NEXT中嵌套网格布局的基础知识,实现了一个企业级仪表板界面。本篇教程将深入探讨嵌套网格布局的进阶技巧,包括复杂布局策略、高级交互效果、动态网格调整等内容,帮助开发者掌握更高级的Grid嵌套用法,打造出更加专业、交互丰富的应用界面。
2. 高级布局策略
2.1 不规则网格布局
在基础教程中,我们使用了规则的网格布局(如2×2、2×1等)。在进阶应用中,我们可以创建不规则的网格布局,使界面更加丰富多样。
2.1.1 使用网格区域(Grid Areas)
通过定义网格区域,我们可以创建复杂的不规则布局:
Grid() {
// 大尺寸卡片(占据2×2区域)
GridItem() {
this.LargeChartCard(this.dashboardData.charts[0])
}
.gridArea('area1')
// 中等尺寸卡片(占据1×2区域)
GridItem() {
this.MediumChartCard(this.dashboardData.charts[1])
}
.gridArea('area2')
// 小尺寸卡片(占据1×1区域)
GridItem() {
this.SmallChartCard(this.dashboardData.charts[2])
}
.gridArea('area3')
// 小尺寸卡片(占据1×1区域)
GridItem() {
this.SmallChartCard(this.dashboardData.charts[3])
}
.gridArea('area4')
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
.rowsTemplate('auto auto auto')
.areas({
area1: { rowStart: 0, rowEnd: 2, columnStart: 0, columnEnd: 2 },
area2: { rowStart: 2, rowEnd: 3, columnStart: 0, columnEnd: 2 },
area3: { rowStart: 0, rowEnd: 1, columnStart: 2, columnEnd: 3 },
area4: { rowStart: 1, rowEnd: 2, columnStart: 2, columnEnd: 3 }
})
.width('100%')
这种布局方式允许我们为不同类型的内容分配不同大小的区域,创建视觉层次感。
2.1.2 混合使用行列模板
我们可以结合使用固定尺寸和弹性尺寸,创建更加灵活的布局:
Grid() {
// 网格项内容...
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 300px')
.rowsTemplate('120px auto 180px')
.width('100%')
这种方式可以确保某些区域保持固定尺寸,而其他区域则根据可用空间自动调整。
2.2 嵌套深度优化
在复杂界面中,Grid嵌套可能会变得很深。过深的嵌套可能导致性能问题和代码可维护性降低。以下是一些优化嵌套深度的策略:
2.2.1 合并相似网格
当多个嵌套网格使用相似的配置时,考虑将它们合并:
// 优化前:两个独立的网格
Grid() { /* 概览卡片 */ }
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
Grid() { /* 图表卡片 */ }
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
// 优化后:合并为一个网格,使用分组
Grid() {
GridItem() {
Text('概览').fontSize(18).fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}.gridSpan({ row: 1, col: 2 })
// 概览卡片
GridItem() { /* 卡片1 */ }
GridItem() { /* 卡片2 */ }
GridItem() { /* 卡片3 */ }
GridItem() { /* 卡片4 */ }
GridItem() {
Text('图表').fontSize(18).fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}.gridSpan({ row: 1, col: 2 })
// 图表卡片
GridItem() { /* 图表1 */ }
GridItem() { /* 图表2 */ }
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
.rowsTemplate('auto auto auto auto auto auto')
2.2.2 使用Builder代替嵌套
在某些情况下,可以使用@Builder装饰器创建复杂组件,而不是使用深层嵌套:
@Builder
ComplexGridSection(title: string, data: any[]) {
Column() {
Text(title)
.fontSize(18)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.margin({ bottom: 12 })
Grid() {
ForEach(data, (item) => {
GridItem() {
// 复杂内容...
}
})
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr 1fr')
.width('100%')
}
.width('100%')
}
// 使用方式
build() {
Column() {
// 直接使用构建器,减少嵌套
this.ComplexGridSection('快捷操作', this.dashboardData.quickActions)
this.ComplexGridSection('最近活动', this.dashboardData.recentActivities)
}
}
2.3 响应式嵌套网格
在不同屏幕尺寸下,我们可能需要调整网格的嵌套结构。以下是一种实现响应式嵌套网格的方法:
@StorageProp('deviceType') deviceType: string = 'phone'
build() {
Column() {
if (this.deviceType === 'phone') {
// 手机布局:垂直堆叠的网格
Grid() { /* 概览卡片 */ }
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
Grid() { /* 图表卡片 */ }
.columnsTemplate('1fr')
Grid() { /* 快捷操作 */ }
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr 1fr')
} else if (this.deviceType === 'tablet') {
// 平板布局:混合布局
Grid() { /* 概览卡片 */ }
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr')
Row() {
Grid() { /* 图表卡片 */ }
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
.layoutWeight(3)
Grid() { /* 快捷操作 */ }
.columnsTemplate('1fr')
.layoutWeight(1)
}
} else {
// 桌面布局:复杂嵌套
Row() {
Column() {
Grid() { /* 概览卡片 */ }
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
Grid() { /* 图表卡片 */ }
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
}
.layoutWeight(3)
Column() {
Grid() { /* 快捷操作 */ }
.columnsTemplate('1fr')
Grid() { /* 最近活动 */ }
.columnsTemplate('1fr')
}
.layoutWeight(1)
}
}
}
}
3. 高级交互效果
3.1 网格项动画
为网格项添加动画效果可以提升用户体验。以下是一些常用的网格项动画技巧:
3.1.1 加载动画
@State gridItemsLoaded: boolean = false
aboutToAppear() {
setTimeout(() => {
this.gridItemsLoaded = true
}, 500)
}
build() {
Grid() {
ForEach(this.dashboardData.charts, (chart: Chart, index) => {
GridItem() {
this.ChartCard(chart)
}
.opacity(this.gridItemsLoaded ? 1 : 0)
.translate({ x: this.gridItemsLoaded ? 0 : 50 })
.animation({
delay: 100 * index,
duration: 300,
curve: Curve.EaseOut
})
})
}
}
3.1.2 交互反馈动画
@Builder
AnimatedGridItem(content: () => void) {
Column() {
content()
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.borderRadius(12)
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFF')
.shadow({
radius: 8,
color: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1)',
offsetX: 0,
offsetY: 2
})
.stateStyles({
pressed: {
scale: { x: 0.95, y: 0.95 },
shadow: {
radius: 4,
color: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1)',
offsetX: 0,
offsetY: 1
}
},
normal: {
scale: { x: 1, y: 1 },
shadow: {
radius: 8,
color: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1)',
offsetX: 0,
offsetY: 2
}
}
})
.animation({
duration: 200,
curve: Curve.EaseInOut
})
}
// 使用方式
GridItem() {
this.AnimatedGridItem(() => {
this.OverviewCard('总销售额', this.dashboardData.overview.totalSales,
$r('app.media.big17'), '#007AFF')
})
}
3.2 网格区域交互
3.2.1 可折叠网格区域
@State isChartSectionExpanded: boolean = true
build() {
Column() {
// 可折叠标题栏
Row() {
Text('图表分析')
.fontSize(18)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
Blank()
Button() {
Image(this.isChartSectionExpanded ?
$r('app.media.arrow_up') : $r('app.media.arrow_down'))
.width(16)
.height(16)
}
.backgroundColor('transparent')
.onClick(() => {
this.isChartSectionExpanded = !this.isChartSectionExpanded
})
}
.width('100%')
.padding(16)
// 可折叠内容
if (this.isChartSectionExpanded) {
Grid() {
ForEach(this.dashboardData.charts, (chart: Chart) => {
GridItem() {
this.ChartCard(chart)
}
})
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
.rowsGap(12)
.columnsGap(12)
.width('100%')
.padding(16)
}
}
.animation({ duration: 300, curve: Curve.EaseInOut })
}
3.2.2 可拖拽调整的网格区域
@State chartSectionHeight: number = 300
@State isDragging: boolean = false
build() {
Column() {
// 图表区域
Column() {
Grid() { /* 图表内容 */ }
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
.width('100%')
// 拖拽手柄
Row() {
Divider().width(40).height(4).borderRadius(2)
}
.width('100%')
.height(20)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.backgroundColor(this.isDragging ? '#E0E0E0' : '#F0F0F0')
.onTouch((event) => {
if (event.type === TouchType.Down) {
this.isDragging = true
} else if (event.type === TouchType.Move && this.isDragging) {
this.chartSectionHeight += event.touches[0].y - event.lastTouches[0].y
// 限制最小和最大高度
this.chartSectionHeight = Math.max(100, Math.min(500, this.chartSectionHeight))
} else if (event.type === TouchType.Up) {
this.isDragging = false
}
})
}
.height(this.chartSectionHeight)
.animation({ duration: this.isDragging ? 0 : 300, curve: Curve.EaseOut })
// 其他内容区域
Grid() { /* 快捷操作和最近活动 */ }
.layoutWeight(1)
}
}
4. 动态网格调整
4.1 根据内容动态调整网格
在某些情况下,我们需要根据内容数量或类型动态调整网格结构:
@State chartCount: number = 4
getColumnsTemplate(): string {
// 根据图表数量动态调整列数
if (this.chartCount <= 2) {
return '1fr'
} else if (this.chartCount <= 4) {
return '1fr 1fr'
} else {
return '1fr 1fr 1fr'
}
}
build() {
Column() {
Grid() {
ForEach(this.dashboardData.charts.slice(0, this.chartCount), (chart: Chart) => {
GridItem() {
this.ChartCard(chart)
}
})
}
.columnsTemplate(this.getColumnsTemplate())
.rowsGap(12)
.columnsGap(12)
.width('100%')
// 控制按钮
Row() {
Button('减少图表')
.onClick(() => {
if (this.chartCount > 1) {
this.chartCount--
}
})
Button('增加图表')
.onClick(() => {
if (this.chartCount < this.dashboardData.charts.length) {
this.chartCount++
}
})
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.margin({ top: 16 })
}
}
4.2 条件渲染网格项
根据不同条件渲染不同的网格项内容:
@State displayMode: 'simple' | 'detailed' = 'simple'
build() {
Column() {
// 显示模式切换
Row() {
Radio({ value: 'simple', group: 'displayMode' })
.checked(this.displayMode === 'simple')
.onChange((isChecked) => {
if (isChecked) {
this.displayMode = 'simple'
}
})
Text('简洁模式').margin({ left: 8, right: 16 })
Radio({ value: 'detailed', group: 'displayMode' })
.checked(this.displayMode === 'detailed')
.onChange((isChecked) => {
if (isChecked) {
this.displayMode = 'detailed'
}
})
Text('详细模式').margin({ left: 8 })
}
.margin({ bottom: 16 })
// 根据模式渲染不同的网格
if (this.displayMode === 'simple') {
Grid() {
ForEach(this.dashboardData.charts, (chart: Chart) => {
GridItem() {
this.SimpleChartCard(chart)
}
})
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr 1fr')
} else {
Grid() {
ForEach(this.dashboardData.charts, (chart: Chart) => {
GridItem() {
this.DetailedChartCard(chart)
}
})
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
}
}
}
5. 高级样式与视觉效果
5.1 网格项层次感
通过阴影、边框和背景色的组合,创建具有层次感的网格项:
@Builder
LayeredGridItem(content: () => void, importance: 'high' | 'medium' | 'low' = 'medium') {
Column() {
content()
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.padding(importance === 'high' ? 20 : (importance === 'medium' ? 16 : 12))
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFF')
.borderRadius(12)
.border({
width: importance === 'high' ? 2 : 0,
color: importance === 'high' ? '#007AFF' : 'transparent',
style: BorderStyle.Solid
})
.shadow({
radius: importance === 'high' ? 16 : (importance === 'medium' ? 8 : 4),
color: `rgba(0, 0, 0, ${importance === 'high' ? 0.15 : (importance === 'medium' ? 0.1 : 0.05)})`,
offsetX: 0,
offsetY: importance === 'high' ? 4 : (importance === 'medium' ? 2 : 1)
})
}
// 使用方式
Grid() {
GridItem() {
this.LayeredGridItem(() => {
// 重要内容
}, 'high')
}
GridItem() {
this.LayeredGridItem(() => {
// 一般内容
}, 'medium')
}
GridItem() {
this.LayeredGridItem(() => {
// 次要内容
}, 'low')
}
}
5.2 网格背景图案
为网格添加背景图案,增强视觉效果:
@Builder
GridWithPattern() {
Stack({ alignContent: Alignment.Center }) {
// 背景图案
Grid() {
ForEach(new Array(20).fill(0), (_, rowIndex) => {
ForEach(new Array(20).fill(0), (_, colIndex) => {
GridItem() {
Circle({ width: 4, height: 4 })
.fill('#EEEEEE')
}
})
})
}
.columnsTemplate('repeat(20, 1fr)')
.rowsTemplate('repeat(20, 1fr)')
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
// 前景内容
Grid() {
// 实际的网格内容
GridItem() { /* 内容1 */ }
GridItem() { /* 内容2 */ }
// ...
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor('#F8F8F8')
}
6. 实际案例:高级仪表板布局
下面是一个结合了上述进阶技巧的高级仪表板布局示例:
build() {
Column() {
// 顶部导航栏(与基础版相同)
// 主要内容区域
Scroll() {
Column() {
// 概览数据(使用动画网格项)
Grid() {
ForEach(Object.entries(this.dashboardData.overview), ([key, value], index) => {
GridItem() {
this.AnimatedGridItem(() => {
this.OverviewCard(
key === 'totalSales' ? '总销售额' :
key === 'totalOrders' ? '总订单数' :
key === 'totalUsers' ? '总用户数' : '总收入',
value as number,
this.getIconForKey(key),
this.getColorForKey(key)
)
})
}
.opacity(this.gridItemsLoaded ? 1 : 0)
.translate({ y: this.gridItemsLoaded ? 0 : 20 })
.animation({
delay: 50 * index,
duration: 300,
curve: Curve.EaseOut
})
})
}
.columnsTemplate(this.getOverviewColumnsTemplate())
.rowsGap(12)
.columnsGap(12)
.width('100%')
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
// 可折叠图表区域
Column() {
// 可折叠标题栏
this.CollapsibleSectionHeader('图表分析', this.isChartSectionExpanded, () => {
this.isChartSectionExpanded = !this.isChartSectionExpanded
})
if (this.isChartSectionExpanded) {
Grid() {
ForEach(this.dashboardData.charts, (chart: Chart, index) => {
GridItem() {
this.LayeredGridItem(() => {
this.ChartCard(chart)
}, index === 0 ? 'high' : 'medium')
}
})
}
.columnsTemplate(this.getChartsColumnsTemplate())
.rowsGap(16)
.columnsGap(16)
.width('100%')
.padding({ top: 12, bottom: 12 })
}
}
.animation({ duration: 300, curve: Curve.EaseInOut })
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
// 快捷操作和最近活动(响应式布局)
if (this.deviceType === 'phone') {
// 手机布局:垂直排列
this.QuickActionsSection()
this.RecentActivitiesSection()
} else {
// 平板/桌面布局:水平排列
Row() {
this.QuickActionsSection()
.layoutWeight(1)
.margin({ right: 8 })
this.RecentActivitiesSection()
.layoutWeight(1)
.margin({ left: 8 })
}
.width('100%')
}
}
.width('100%')
.padding(16)
}
.layoutWeight(1)
.backgroundColor('#F8F8F8')
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
7. 总结
本教程深入探讨了HarmonyOS NEXT中嵌套网格布局的进阶技巧,包括不规则网格布局、嵌套深度优化、响应式嵌套网格、高级交互效果、动态网格调整以及高级样式与视觉效果等内容。通过这些进阶技巧,开发者可以创建出更加灵活、交互丰富、视觉效果出色的应用界面。
- 0回答
- 5粉丝
- 0关注
