175.[HarmonyOS NEXT 实战案例七:Grid] 嵌套网格布局基础篇:打造企业级仪表板界面
2025-06-30 22:58:04
299次阅读
0个评论
[HarmonyOS NEXT 实战案例七:Grid] 嵌套网格布局基础篇:打造企业级仪表板界面
项目已开源,开源地址: https://gitcode.com/nutpi/HarmonyosNextCaseStudyTutorial , 欢迎fork & star
效果演示
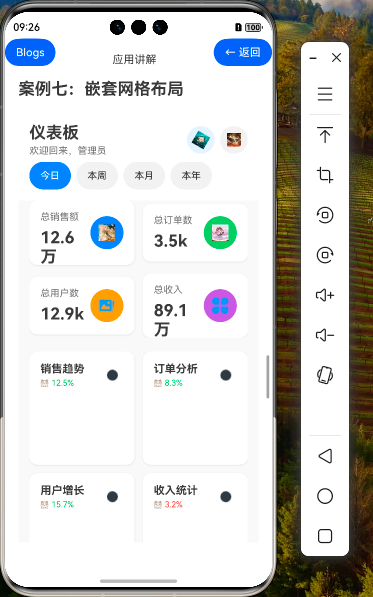
1. 引言
在现代应用开发中,仪表板(Dashboard)界面是企业级应用的重要组成部分,它能够直观地展示关键数据和指标,帮助用户快速了解业务状况。HarmonyOS NEXT提供的Grid组件具有强大的布局能力,特别是通过嵌套使用,可以实现复杂的界面结构。本教程将详细讲解如何使用Grid组件的嵌套功能,打造一个功能完善、布局合理的企业级仪表板界面。
2. 数据模型设计
2.1 仪表板数据结构
在开始实现界面之前,我们需要设计合适的数据模型来支持仪表板的各个部分。以下是我们定义的数据接口:
interface DashboardData {
overview: Overview;
charts: Chart[];
quickActions: QuickAction[];
recentActivities: RecentActivity[];
}
interface Overview {
totalSales: number;
totalOrders: number;
totalUsers: number;
totalRevenue: number;
}
interface Chart {
id: number;
title: string;
type: 'line' | 'bar' | 'area' | 'pie';
data: number[];
color: string;
trend: 'up' | 'down';
percentage: number;
}
interface QuickAction {
id: number;
title: string;
icon: ResourceStr;
color: string;
count?: number; // 可选,部分项目没有计数
}
interface RecentActivity {
id: number;
title: string;
description: string;
time: string;
type: 'user' | 'payment' | 'order' | 'system';
icon: ResourceStr;
}
这些接口定义了仪表板的四个主要部分:
- 概览数据(Overview):包含总销售额、总订单数、总用户数和总收入等关键指标
- 图表数据(Charts):包含各种类型的图表,如销售趋势、订单分析等
- 快捷操作(QuickActions):提供常用功能的快速访问入口
- 最近活动(RecentActivities):显示系统中的最新动态
2.2 示例数据初始化
为了演示效果,我们初始化了一组示例数据:
@State dashboardData: DashboardData = {
overview: {
totalSales: 125680,
totalOrders: 3456,
totalUsers: 12890,
totalRevenue: 890560
},
charts: [
{
id: 1,
title: '销售趋势',
type: 'line',
data: [120, 150, 180, 200, 170, 220, 250],
color: '#007AFF',
trend: 'up',
percentage: 12.5
},
// 其他图表数据...
],
quickActions: [
{
id: 1,
title: '新订单',
icon: $r('app.media.big26'),
color: '#007AFF',
count: 23
},
// 其他快捷操作...
],
recentActivities: [
{
id: 1,
title: '新用户注册',
description: '用户 张三 完成注册',
time: '2分钟前',
type: 'user',
icon: $r('app.media.big19')
},
// 其他活动数据...
]
}
3. 辅助功能实现
3.1 数字格式化
为了更好地展示数据,我们实现了一个数字格式化函数,将大数字转换为更易读的形式:
formatNumber(num: number): string {
if (num >= 100000) {
return (num / 10000).toFixed(1) + '万'
} else if (num >= 1000) {
return (num / 1000).toFixed(1) + 'k'
}
return num.toString()
}
3.2 数据刷新功能
仪表板通常需要定期刷新数据,我们实现了一个简单的刷新功能:
@State refreshing: boolean = false
refreshData() {
this.refreshing = true
setTimeout(() => {
this.refreshing = false
console.log('数据刷新完成')
}, 2000)
}
4. 组件构建器实现
为了实现界面的模块化和代码复用,我们使用@Builder装饰器创建了两个重要的构建器:
4.1 概览卡片构建器
@Builder
OverviewCard(title: string, value: number, icon: Resource, color: string) {
Column() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text(title)
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor('#666666')
Text(this.formatNumber(value))
.fontSize(24)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.fontColor('#333333')
.margin({ top: 8 })
}
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Start)
.layoutWeight(1)
Row() {
Image(icon)
.width(24)
.height(24)
.fillColor('#FFFFFF')
}
.width(48)
.height(48)
.borderRadius(24)
.backgroundColor(color)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
.width('100%')
}
.width('100%')
.padding(16)
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFF')
.borderRadius(12)
.shadow({
radius: 8,
color: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1)',
offsetX: 0,
offsetY: 2
})
}
4.2 图表卡片构建器
@Builder
ChartCard(chart:Chart) {
Column() {
// 图表头部
Row() {
Column() {
Text(chart.title)
.fontSize(16)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.fontColor('#333333')
Row() {
Image(chart.trend === 'up' ? $r('app.media.01') :
chart.trend === 'down' ? $r('app.media.02') : $r('app.media.03'))
.width(12)
.height(12)
.fillColor(chart.trend === 'up' ? '#34C759' :
chart.trend === 'down' ? '#FF3B30' : '#8E8E93')
Text(`${Math.abs(chart.percentage)}%`)
.fontSize(12)
.fontColor(chart.trend === 'up' ? '#34C759' :
chart.trend === 'down' ? '#FF3B30' : '#8E8E93')
.margin({ left: 4 })
}
.margin({ top: 4 })
}
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Start)
.layoutWeight(1)
Button() {
Image($r('app.media.more_icon'))
.width(16)
.height(16)
.fillColor('#8E8E93')
}
.width(32)
.height(32)
.borderRadius(16)
.backgroundColor('transparent')
}
.width('100%')
.margin({ bottom: 16 })
// 简化的图表显示
Row() {
ForEach(chart.data, (value:string, index) => {
Column() {
Text(value)
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor('#333333')
}
.height(80)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.End)
.margin({ right: index < chart.data.length - 1 ? 4 : 0 })
})
}
.width('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceEvenly)
}
.width('100%')
.padding(16)
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFF')
.borderRadius(12)
.shadow({
radius: 8,
color: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1)',
offsetX: 0,
offsetY: 2
})
}
5. 页面结构与嵌套网格实现
5.1 页面整体结构
仪表板页面的整体结构如下:
build() {
Column() {
// 顶部导航栏
// 时间范围选择
// 主要内容区域(嵌套网格)
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor('#F8F8F8')
}
5.2 顶部导航栏实现
顶部导航栏包含标题、欢迎信息和操作按钮:
// 顶部导航栏
Row() {
Column() {
Text('仪表板')
.fontSize(24)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.fontColor('#333333')
Text('欢迎回来,管理员')
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor('#666666')
.margin({ top: 4 })
}
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Start)
.layoutWeight(1)
Row() {
Button() {
Image(this.refreshing ? $r('app.media.big23') : $r('app.media.big21'))
.width(20)
.height(20)
.fillColor('#007AFF')
.rotate({ angle: this.refreshing ? 360 : 0 })
.animation({
duration: 1000,
iterations: this.refreshing ? -1 : 1,
curve: Curve.Linear
})
}
.width(40)
.height(40)
.borderRadius(20)
.backgroundColor('rgba(0, 122, 255, 0.1)')
.margin({ right: 8 })
.onClick(() => {
this.refreshData()
})
Button() {
Image($r('app.media.big20'))
.width(20)
.height(20)
.fillColor('#333333')
}
.width(40)
.height(40)
.borderRadius(20)
.backgroundColor('#F0F0F0')
}
}
.width('100%')
.padding({ left: 16, right: 16, top: 16, bottom: 8 })
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFF')
5.3 时间范围选择实现
时间范围选择器允许用户切换不同的时间维度:
// 时间范围选择
Row() {
ForEach(this.timeRanges, (range:string, index) => {
Button(range)
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor(this.selectedTimeRange === range ? '#FFFFFF' : '#333333')
.backgroundColor(this.selectedTimeRange === range ? '#007AFF' : '#F0F0F0')
.borderRadius(16)
.padding({ left: 16, right: 16, top: 8, bottom: 8 })
.margin({ right: index < this.timeRanges.length - 1 ? 8 : 0 })
.onClick(() => {
this.selectedTimeRange = range
})
})
Blank()
}
.width('100%')
.padding({ left: 16, right: 16, bottom: 16 })
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFF')
5.4 嵌套网格实现
这是本教程的核心部分,我们使用多层嵌套的Grid组件来实现复杂的布局:
5.4.1 概览数据网格
// 概览数据网格
Grid() {
GridItem() {
this.OverviewCard('总销售额', this.dashboardData.overview.totalSales,
$r('app.media.big17'), '#007AFF')
}
GridItem() {
this.OverviewCard('总订单数', this.dashboardData.overview.totalOrders,
$r('app.media.big30'), '#34C759')
}
GridItem() {
this.OverviewCard('总用户数', this.dashboardData.overview.totalUsers,
$r('app.media.album_icon'), '#FF9500')
}
GridItem() {
this.OverviewCard('总收入', this.dashboardData.overview.totalRevenue,
$r('app.media.category_icon'), '#AF52DE')
}
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
.rowsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
.rowsGap(12)
.columnsGap(12)
.width('100%')
.height(200)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
这个网格使用2×2的布局,展示四个关键指标卡片。通过columnsTemplate和rowsTemplate属性,我们定义了网格的行列结构。
5.4.2 图表区域网格
// 图表区域网格
Grid() {
ForEach(this.dashboardData.charts, (chart: Chart) => {
GridItem() {
this.ChartCard(chart)
}
})
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
.rowsGap(12)
.columnsGap(12)
.width('100%')
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
图表区域使用2列布局,行数根据图表数量动态确定。
5.4.3 快捷操作网格
Grid() {
ForEach(this.dashboardData.quickActions, (action:QuickAction) => {
GridItem() {
Column() {
Stack({ alignContent: Alignment.TopEnd }) {
Row() {
Image(action.icon)
.width(24)
.height(24)
.fillColor('#FFFFFF')
}
.width(48)
.height(48)
.borderRadius(24)
.backgroundColor(action.color)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
if (action.count !== undefined && action.count > 0) {
Text(action.count.toString())
.fontSize(10)
.fontColor('#FFFFFF')
.backgroundColor('#FF3B30')
.borderRadius(8)
.padding({ left: 4, right: 4, top: 2, bottom: 2 })
.margin({ top: -4, right: -4 })
}
}
Text(action.title)
.fontSize(12)
.fontColor('#333333')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.margin({ top: 8 })
}
.width('100%')
.padding(8)
}
.onClick(() => {
console.log(`点击快捷操作: ${action.title}`)
})
})
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr 1fr')
.rowsGap(16)
.columnsGap(8)
.width('100%')
快捷操作区域使用3列网格布局,每个网格项包含一个操作按钮和标题。
6. 嵌套网格的优势与技巧
6.1 嵌套网格的优势
| 优势 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 布局灵活性 | 通过嵌套Grid,可以在不同区域使用不同的网格配置 |
| 代码组织 | 将界面分解为多个网格区域,使代码结构更清晰 |
| 响应式适配 | 每个网格区域可以独立配置响应式行为 |
| 维护性 | 修改某一区域时,不会影响其他区域的布局 |
6.2 嵌套网格使用技巧
- 合理划分区域:根据内容的逻辑关系,将界面划分为不同的区域,每个区域使用独立的Grid
- 统一间距:保持不同网格之间的间距一致,创造统一的视觉效果
- 灵活使用模板:根据内容特点,为每个网格设置合适的行列模板
- 组合其他容器:Grid可以与Row、Column等容器组合使用,实现更复杂的布局
7. 总结
在下一篇教程中,我们将深入探讨嵌套网格布局的进阶技巧,包括动态调整网格结构、高级交互效果和性能优化等内容,敬请期待!
00
- 0回答
- 5粉丝
- 0关注
